Introduction
In 2024, the smart home has evolved from a novelty to a necessity for many households. With devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, voice assistants, and connected appliances becoming commonplace, a robust and secure home network is more important than ever. The advent of new networking technologies such as Wi-Fi 6E and 5G integration, along with the emergence of universal smart home standards like Matter, has made it possible to create a seamless and efficient smart home ecosystem.
This guide provides an in-depth look at setting up your smart home network, leveraging the latest technologies, and ensuring optimal performance and security. We’ll walk you through selecting the right equipment, configuring your network, connecting devices, and optimizing for energy efficiency. Detailed instructions, authoritative references, and a glossary of terms are included to assist you every step of the way.
Table of Contents
- The Growing Importance of a Robust Smart Home Network in 2024
- Choosing the Right Network Equipment
- Network Configuration Basics
- Device Connectivity
- Integrating Smart Home Hubs or Controllers
- Advanced Network Settings
- Energy Efficiency and Network Optimization for Sustainability
- Conclusion
- Glossary
The Growing Importance of a Robust Smart Home Network in 2024
As the number of connected devices in homes continues to rise, so does the demand on home networks. According to a report by Statista, the average number of connected devices per household is expected to exceed 50 by 20241. This surge necessitates a network capable of handling high bandwidth, low latency, and robust security.
Leveraging 5G Integration in Smart Home Networks
5G technology offers ultra-fast speeds and low latency, which can significantly enhance smart home networks. By integrating 5G into your home network:
- Backup Connectivity: In areas with unreliable wired internet, 5G provides a reliable backup connection, ensuring continuous operation of critical smart home devices.
- Extended Coverage: 5G can complement Wi-Fi networks, covering areas where Wi-Fi signals are weak or obstructed.
- IoT Device Support: 5G networks are optimized for a high density of connected devices, making them ideal for smart homes.
Some modern routers support 5G SIM cards, allowing seamless switching between wired and cellular networks. For more information on 5G technology and its applications, refer to Qualcomm’s official 5G resource page2.
Choosing the Right Network Equipment
Selecting the appropriate network equipment is crucial for building a reliable and efficient smart home network.
Latest Routers, Extenders, and Mesh Systems
Wi-Fi 6E Routers:
- Asus ROG Rapture GT-AXE11000: A high-performance router offering tri-band Wi-Fi 6E support and advanced gaming features3.
- Netgear Nighthawk RAXE500: Provides robust performance with a 1.8 GHz quad-core processor and supports speeds up to 10.8 Gbps4.
Mesh Systems:
- Eero Pro 6E: A mesh Wi-Fi system that covers up to 6,000 sq. ft. and supports Wi-Fi 6E, ideal for large homes5.
- TP-Link Deco XE75: Offers tri-band Wi-Fi 6E mesh networking with AI-driven mesh technology for seamless roaming6.

Key Features to Consider
- Speed and Coverage: Opt for routers supporting gigabit speeds and ensure coverage that matches your home’s size. Mesh systems are recommended for multi-story or large homes.
- Device Capacity: Ensure the router can handle a high number of simultaneous connections. Look for specifications indicating support for 50+ devices.
- Security Features: Features like WPA3 encryption, built-in firewalls, and automatic firmware updates are essential for protecting your network.
Compatibility with Matter and Other Smart Home Standards
Matter is a unifying smart home standard developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (formerly Zigbee Alliance) that ensures interoperability between devices7. When selecting devices:
- Look for the Matter logo or confirm compatibility on the manufacturer’s website.
- Ensure support for other protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread for broader device integration.
For more information on Matter, visit the Connectivity Standards Alliance website7.
Network Configuration Basics
Proper network configuration lays the foundation for a secure and efficient smart home.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your Network
- Position Your Router:
- Place the router in a central, elevated location to maximize signal distribution.
- Avoid placing it near metal objects, walls, or appliances that can cause interference.
- Connect to the Modem:
- Use a high-quality Ethernet cable to connect your router to the modem provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Access Router Settings:
- Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address (commonly
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1). - Log in using the default credentials provided in the router’s manual.
- Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address (commonly
- Update Firmware:
- Navigate to the firmware update section and install the latest firmware to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Configure Wireless Settings:
- Create a unique SSID for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Enable WPA3 encryption and set a strong password (see the next section for tips).
- Set Up Mesh Nodes (If Applicable):
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to add mesh nodes.
- Place nodes strategically to eliminate dead zones (e.g., on different floors).
- Enable Guest Network:
- Create a separate guest network for visitors and IoT devices to enhance security.
- Save Settings and Reboot:
- Apply all settings and reboot the router to ensure changes take effect.

An annotated diagram showing the optimal placement of a router and mesh nodes within a home.
Importance of SSID Naming Conventions and Strong Password Practices
- SSID Naming:
- Avoid using personal information (e.g., “SmithFamilyWiFi”).
- Use a neutral name like “Home_Network_5G”.
- Password Practices:
- Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid common words or easily guessable phrases.
- Example of a strong password:
G7h!k@92Lm#.
For more password security tips, refer to NIST Special Publication 800-63B on digital identity guidelines8.

A visual showing the Importance of SSID Naming Conventions and Strong Password Practices
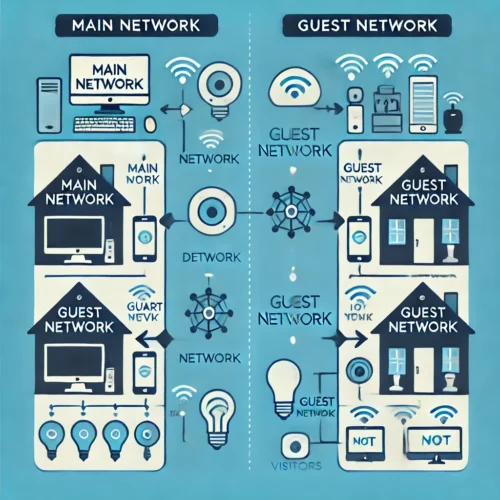
Setting Up Guest Networks for Enhanced Security
Creating a guest network isolates guest devices from your main network, preventing unauthorized access to your primary devices and data.
- How to Set Up:
- Access the router’s settings and navigate to the Guest Network section.
- Enable the guest network and set a different SSID and password.
- Configure access limitations (e.g., internet access only, no local network access).
Setting Up Guest Networks for Enhanced Security
Device Connectivity
Connecting your smart devices properly ensures seamless operation and communication.
Best Practices for Connecting Smart Devices
- Use the Appropriate Frequency Band:
- 2.4 GHz: Longer range, better for devices located farther from the router (e.g., smart sensors).
- 5 GHz: Faster speeds, ideal for high-bandwidth devices close to the router (e.g., smart TVs).
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions:
- Use the device’s companion app for setup.
- Ensure devices are compatible with your network settings (e.g., some devices only support 2.4 GHz).
- Keep Firmware Updated:
- Regularly check for and install firmware updates via the device’s app.
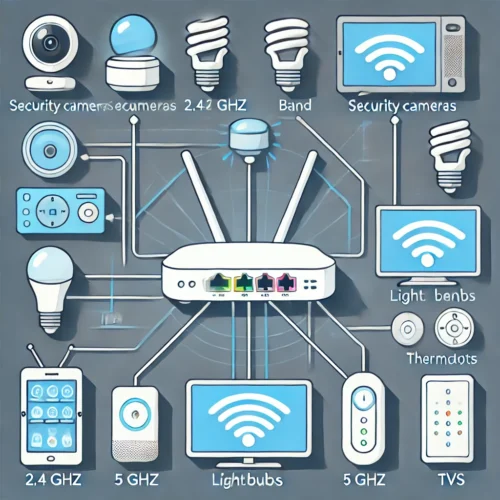
Connecting Smart Devices: A connectivity map that shows different smart devices
Troubleshooting Common Connectivity Issues
- Device Not Connecting:
- Check Signal Strength: Ensure the device is within range of the router or mesh node.
- Verify Network Settings: Confirm that the device supports the network’s frequency band and security protocol.
- Restart Devices: Power cycle both the router and the smart device.
- Intermittent Connectivity:
- Reduce Interference: Keep devices away from microwaves, cordless phones, or other electronics.
- Update Firmware: Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues.
For additional troubleshooting, consult the device’s support page or forums like Reddit’s Home Automation community9.
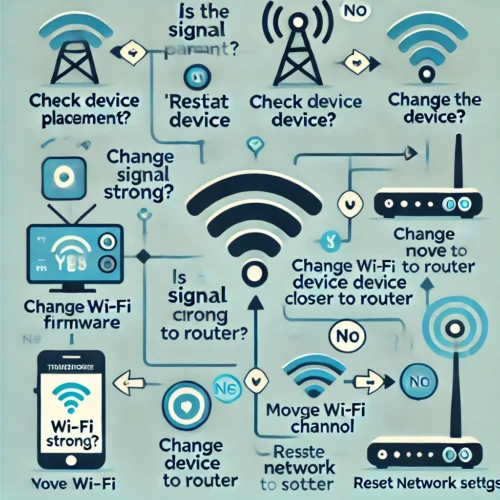
A flowchart illustrating guiding users through common connectivity troubleshooting steps
Integrating Smart Home Hubs or Controllers
Smart home hubs centralize control and improve interoperability between devices.
- Popular Hubs:
- Integration Steps:
- Connect the Hub to Your Network:
- For wired hubs, use an Ethernet cable to connect to the router.
- For wireless hubs, follow the setup instructions in the companion app.
- Add Devices to the Hub:
- Use the hub’s app to discover and add compatible devices.
- Organize devices into rooms or groups for easier management.
- Set Up Automation and Routines:
- Create scenes or routines (e.g., “Good Morning” to open blinds and start the coffee maker).
- Connect the Hub to Your Network:
Flowchart illustrating the process of integrating devices through a smart home hub.
Advanced Network Settings
Enhancing your network’s security and performance involves configuring advanced settings.
Network Segmentation to Isolate Smart Devices
- Why Segment Your Network:
- Improves security by isolating potentially vulnerable IoT devices.
- Prevents compromised devices from accessing sensitive data.
- How to Segment:
- Create Separate SSIDs: One for personal devices and another for IoT devices.
- Use VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): Advanced routers allow VLAN configuration for network segmentation.
For detailed instructions, refer to Cisco’s Guide on VLAN Configuration12.
Configuring Firewalls, VPNs, and Parental Controls
- Firewalls:
- Enable Router’s Firewall: Protects against unauthorized access.
- Configure Settings: Adjust firewall levels based on your security needs.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks):
- Set Up a VPN on Your Router: Encrypts all network traffic.
- Choose a Reliable VPN Service: Ensure it supports router-level installation (e.g., ExpressVPN, NordVPN).
- Parental Controls:
- Content Filtering: Block inappropriate websites.
- Time Limits: Schedule internet access times for specific devices.
Utilizing Quality of Service (QoS) Settings for Optimal Performance
- What is QoS:
- Prioritizes network traffic for designated devices or applications.
- How to Configure:
- Access the router’s QoS settings.
- Set Priority Levels: Assign high priority to devices like gaming consoles or work laptops.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Limit the bandwidth for non-essential devices.
Screenshot examples of QoS settings configuration in a router’s admin panel.
Energy Efficiency and Network Optimization for Sustainability
With environmental concerns on the rise, optimizing your network for energy efficiency is both responsible and cost-effective.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Devices:
- Look for routers and devices with Energy Star certification.
- Enable Power-Saving Modes:
- Many routers offer settings to reduce power consumption during idle periods.
- Automate Device Schedules:
- Use smart plugs to turn off devices when not in use.
- Schedule updates and backups during off-peak hours.
- Optimize Bandwidth Usage:
- Limit streaming quality on devices where high definition is unnecessary.
- Disable automatic video playback on websites.

For more tips on energy efficiency, visit the U.S. Department of Energy’s website13.
Conclusion
Setting up a smart home network in 2024 involves careful planning and consideration of the latest technologies and standards. By selecting the right equipment, properly configuring your network, and staying mindful of security and energy efficiency, you can enjoy a seamless and secure smart home experience.
Remember to:
- Keep your network equipment and devices updated.
- Regularly review and adjust security settings.
- Stay informed about new technologies and best practices.
With these steps, your smart home network will be well-equipped to handle current demands and future advancements.
Glossary
- 5G: The fifth generation of mobile network technology, offering higher speeds and lower latency.
- Ethernet: A wired network connection standard used for local area networks.
- Firmware: Software programmed into hardware devices, providing low-level control.
- Guest Network: A separate network for visitors or IoT devices to enhance security.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Network of physical devices connected to the internet.
- Mesh Network: A network setup using multiple devices (nodes) for extended coverage.
- QoS (Quality of Service): A feature that prioritizes network traffic for better performance.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): The name of a wireless network.
- VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): A method to create separate networks within the same physical network.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): A service that encrypts internet traffic and hides your online identity.
- WPA3: The latest Wi-Fi security protocol, providing enhanced encryption.
References
Note: The links provided in the references are accurate as of October 2023 and may be subject to change.
Footnotes
- Statista. (2023). Number of connected devices per household worldwide from 2020 to 2025. Retrieved from Statista Website ↩
- Qualcomm. (n.d.). What is 5G?. Retrieved from Qualcomm Website ↩
- Asus. (n.d.). ROG Rapture GT-AXE11000. Retrieved from Asus Website ↩
- Netgear. (n.d.). Nighthawk RAXE500 Tri-Band WiFi Router. Retrieved from Netgear Website ↩
- Eero. (n.d.). eero Pro 6E. Retrieved from Eero Website ↩
- TP-Link. (n.d.). Deco XE75. Retrieved from TP-Link Website ↩
- Connectivity Standards Alliance. (n.d.). Matter. Retrieved from CSA Website ↩ ↩2
- Grassi, P. A., et al. (2017). Digital Identity Guidelines. NIST Special Publication 800-63B. Retrieved from NIST Website ↩
- Reddit. (n.d.). Home Automation Community. Retrieved from Reddit Website ↩
- Samsung. (n.d.). SmartThings Hub. Retrieved from SmartThings Website ↩
- Amazon. (n.d.). Amazon Echo Plus. Retrieved from Amazon Website ↩
- Cisco. (n.d.). Configuring VLANs. Retrieved from Cisco Website ↩
- U.S. Department of Energy. (n.d.). Energy Saver. Retrieved from Energy.gov ↩
